| Index |
|
Avian
Influenza
|
|
|
|
Anti-bacterial Barrier
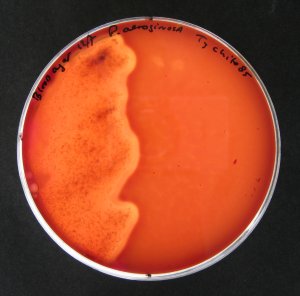
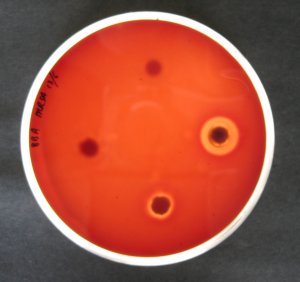
cream A highly effective barrier cream/powder has been researched by the University of Lincoln, to help protect against environmental contaminants. This may be of particular use to animals susceptible to for example Mud Fever or MRSA infections. It has been
shown to have anti-bacterial and anti-fungal properties with
no known side effects. Some indirect evidence indicates haemostatic
and wound healing properties. The cream is
based on the anti-microbial properties of silver bound to an inert
carrier. Together they provide an effective barrier against a wide
range of micro-organisms as well as support wound healing. No evidence
has yet been found of resistance development against the active
ingredient. Just a few of
the organisms it has been shown to be effective against:
A powder version has been designed to be applied to:
More formal research results will be published on this site. Currently field studies to test the efficacy of the barrier creams against environmental contaminants are planned. Any one interested in participating please go to www.lincoln.ac.uk/dbs/researchprojects-participate for more information
|
|
|
 A------------B
A------------B